CI/CD GOAT Writeup
CI/CD GOAT 是一个用于帮助工程师和安全技术人员学习和实践 CI/CD 安全技术的靶场,这一组十一个不同难度梯度的独立挑战基本涵盖了 OWASP Top 10 CI/CD Security Risks
部署
Linux & Mac
1 | curl -o cicd-goat/docker-compose.yaml --create-dirs https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cider-security-research/cicd-goat/main/docker-compose.yaml |
Windows (Powershell)
1 | mkdir cicd-goat; cd cicd-goat |
Take the Challenge
靶场启动后靶场 IP 共有 3 个地址可以访问,分别是
| Platform | Port | Default Username | Default Password | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTFd | 8000 | alice | alice | 提交 Flag 的比赛平台 |
| Jenkins | 8080 | alice | alice | CI/CD 的 pipeline 管理平台 |
| Gitea | 3000 | thealice | thealice | 自建 Gitea 代码托管平台 |
| GitLab | 4000 | alice | alice12345 | 自建 Gitlab 代码托管平台 |
Default Username/Password 的含义是,还存在其它的账户可用于登录,并且事实上还不少,基本都是弱密码,可简单爆破得到,比较重要的管理员账户及其口令为
Platform Admin Username Admin Password CTFd admin ciderland5# Jenkins admin ciderland5# Gitea red_queen ciderland5# Gitlab root ciderland5# 可以登陆这些账号查看管理员是如何配置环境的,以及作弊直接更改 pipeline 拿 flag
在这个靶场中的威胁建模中,攻击者(我们)被认为是恶意的开发者或者某些已经获取了在代码托管平台上的仓库的读/写权限,并且在 Jenkins 中拥有读权限作为立足点的黑客,攻击者的目的是通过攻击 SCM 与 CI/CD 平台窃取他人的秘密凭证或进行供应链投毒。因此,每一个挑战的 Flag 基本都是 CI/CD 环境中以环境变量形式存在的 secret token,每一个挑战的基本流程基本都是 git clone 攻击者想要攻击的仓库,并通过 PR 等形式触发 CI/CD 并查看 CI/CD 平台的控制台日志输出获取想要窃取的信息。
OWASP Top 10 CI/CD Security Risks 简介
CI/CD,或者说持续集成/部署技术能够将代码从工程师的开发环境自动化且高效地集成到生产环境,是任何现代软件组织的心脏。而随着 DevOps 学科,微服务架构,云技术与各类基础设施的发展,CI/CD 系统得以更快、更灵活也更便捷地完成软件交付的工作。鉴于 CI/CD 服务的广泛使用及其重要性,越来越多不同规模的攻击者都将注意力转移到了 CI/CD 技术上,并发现了诸多基于 CI/CD 技术得以重塑或拓展的攻击面。
OWASP Foundation 在 2022 年发布了 OWASP CI/CD 十大安全风险,其具体风险列表如下
| Risk 风险 | Details 详情 |
|---|---|
| Insufficient Flow Control Mechanisms 不足的流程控制机制 | Insufficient-Flow-Control-Mechanisms |
| Inadequate Identity and Access Management 不当的身份识别和访问管理 | Inadequate-Identity-And-Access-Management |
| Dependency Chain Abuse 依赖链滥用 | Dependency-Chain-Abuse |
| Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE) 管道投毒执行 | Poisoned-Pipeline-Execution |
| Insufficient PBAC (Pipeline-Based Access Controls) 基于流水线的访问控制不足 | Insufficient-PBAC |
| Insufficient Credential Hygiene 凭据清理不足 | Insufficient-Credential-Hygiene |
| Insecure System Configuration 不安全的系统配置 | Insecure-System-Configuration |
| Ungoverned Usage of 3rd Party Services 第三方服务的不受控使用 | Ungoverned-Usage-of-3rd-Party-Services |
| Improper Artifact Integrity Validation 不正确的工件完整性验证 | Improper-Artifact-Integrity-Validation |
| Insufficient Logging and Visibility 日志记录和可见性不足 | Insufficient-Logging-And-Visibility |
更多 DevSecOps 的基础知识或者说是完成这个靶场所需要的前置知识可见文末 参考链接
Writeup
White Rabbit
Risks
- CICD-SEC-4: Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE)
- CICD-SEC-6: Insufficient Credential Hygiene
Analysis
攻击者对这个仓库具有读写权限,CI/CD 通过 Pr 触发,并由 Jenkinsfile 控制 CI/CD 流。那么显而易见,攻击者能够进行 PPE 攻击,并且是直接 PPE 攻击 (D-PPE)。审计根目录下的 Jenkinsfile
1 | pipeline { |
不了解 Jenkinsfile 的语法的话可以通过文末提供的 链接 花五分钟快速学一下
攻击者能够(结合 hint)发现 secret 存在全局范围的 Jenkins 凭证存储中,因此只需要在 Jenkinsfile 中添加读取 flag 的代码即可获取 flag
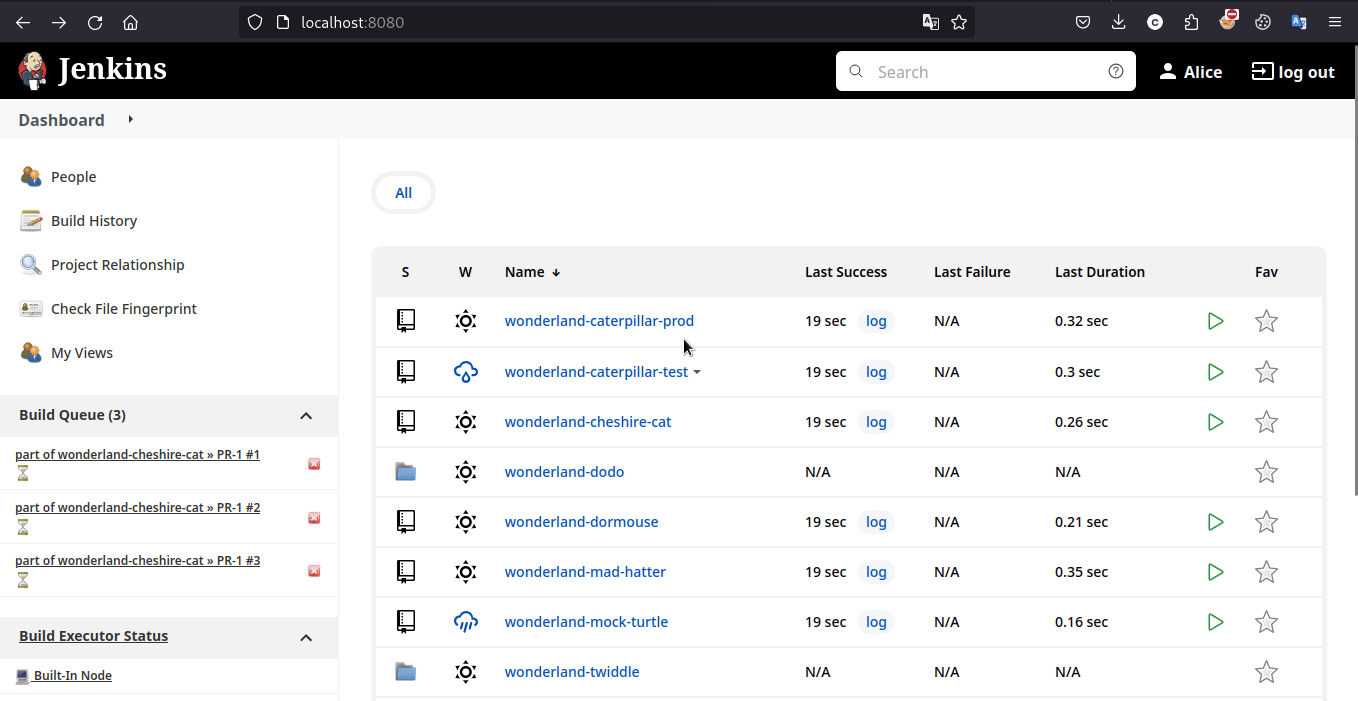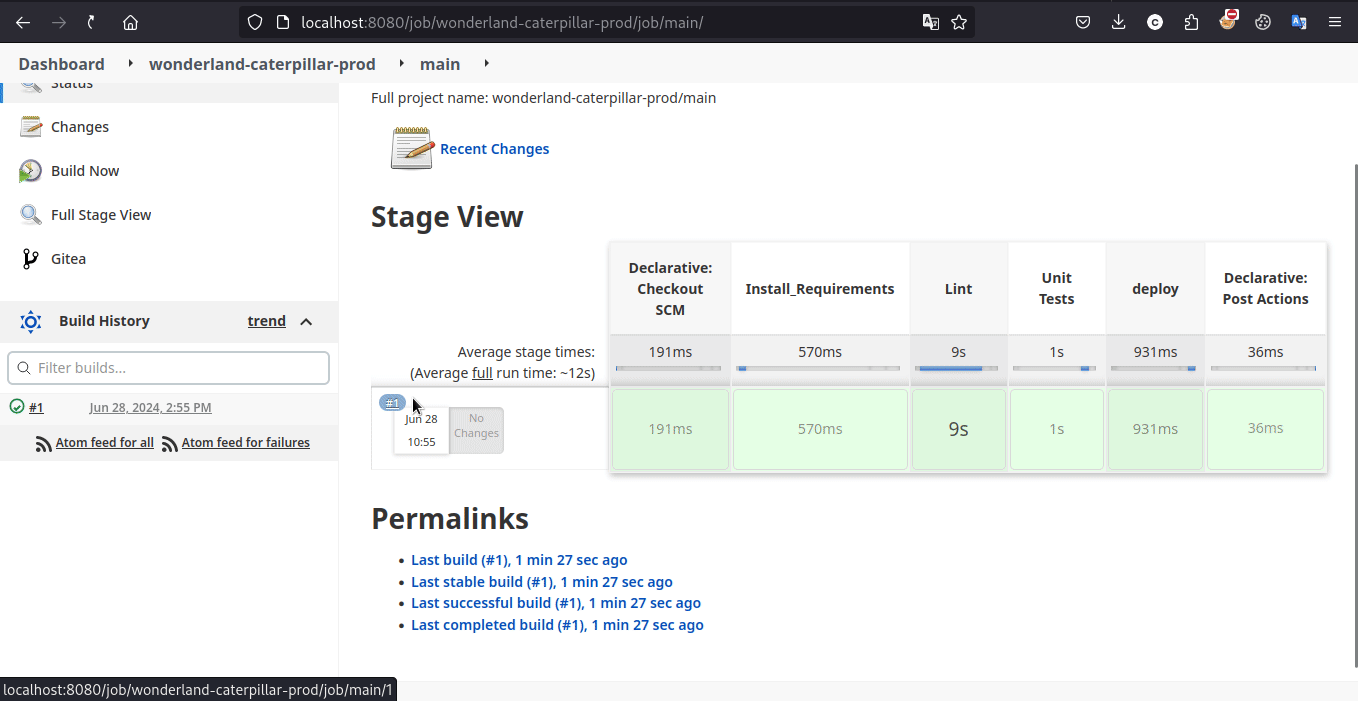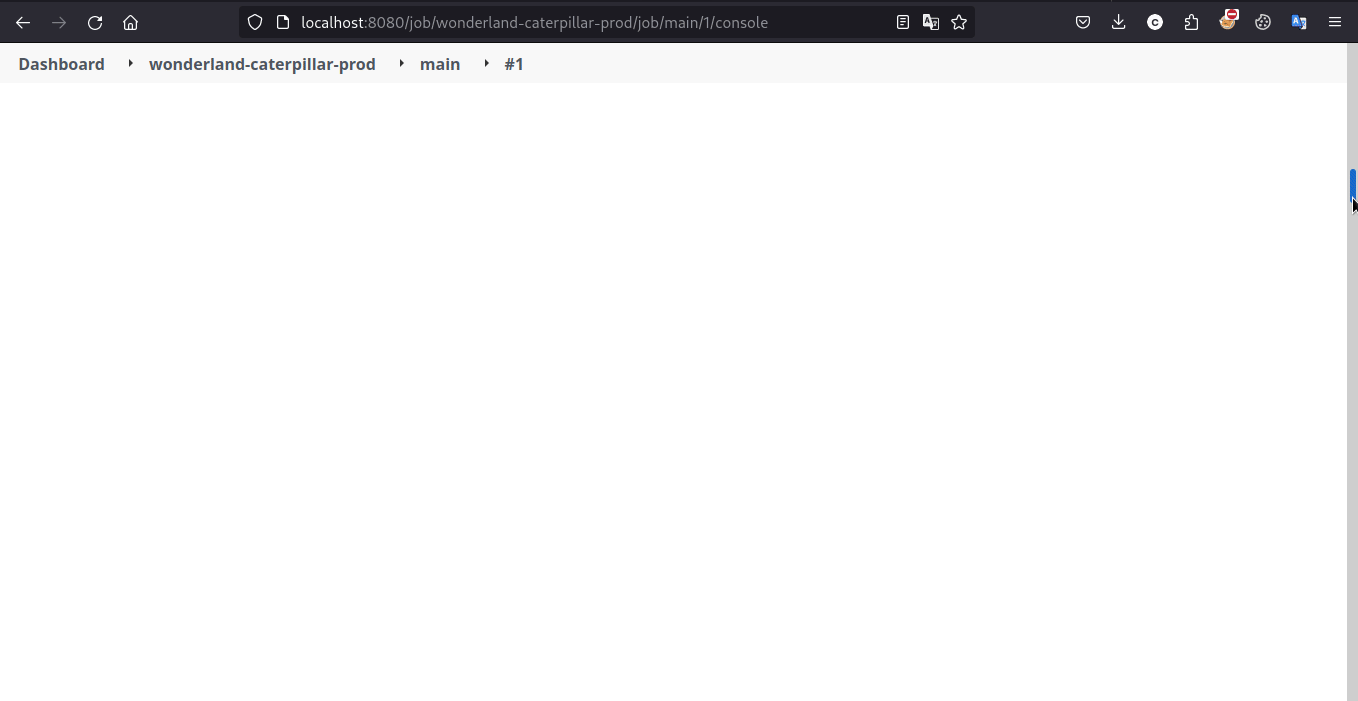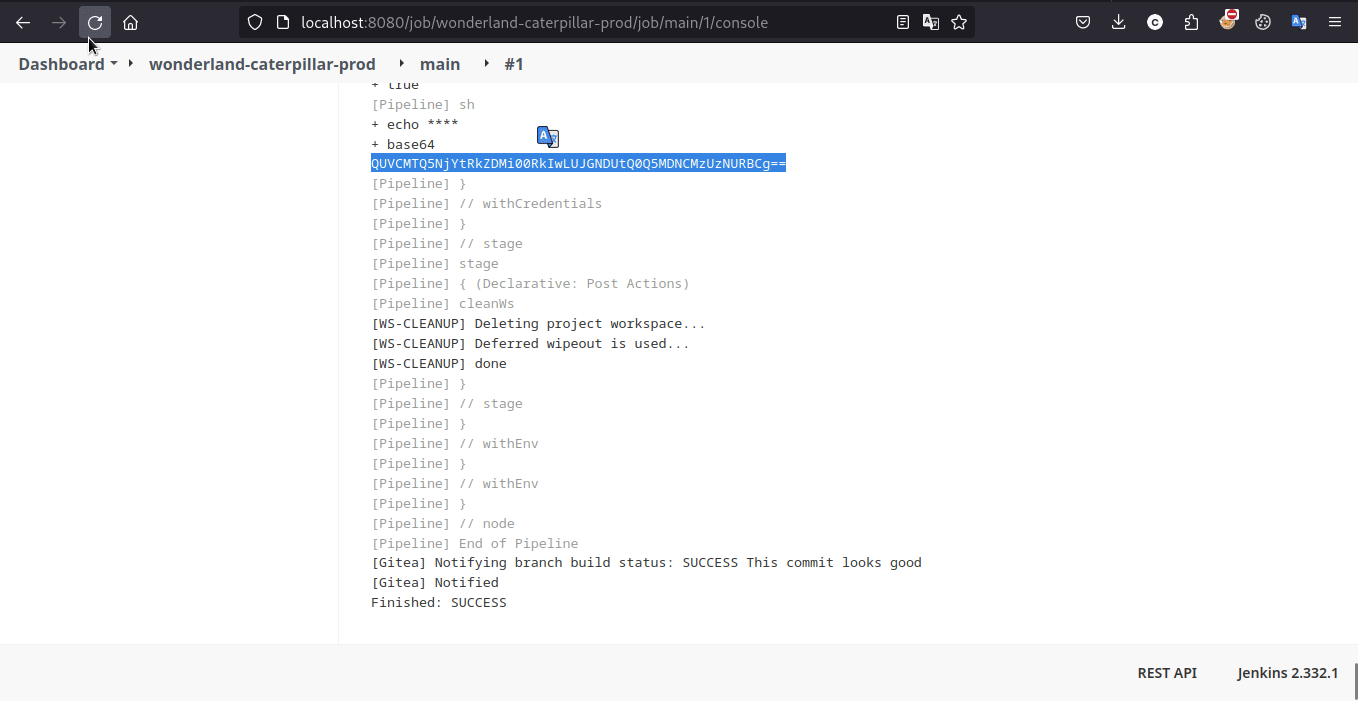
需要注意的是靶场启用了 Masks Password 插件,因此直接输出的 flag 将会被屏蔽,需要编码输出。此后的大部分题目也需要编码输出处理。
参考以下流程即可拿到 flag
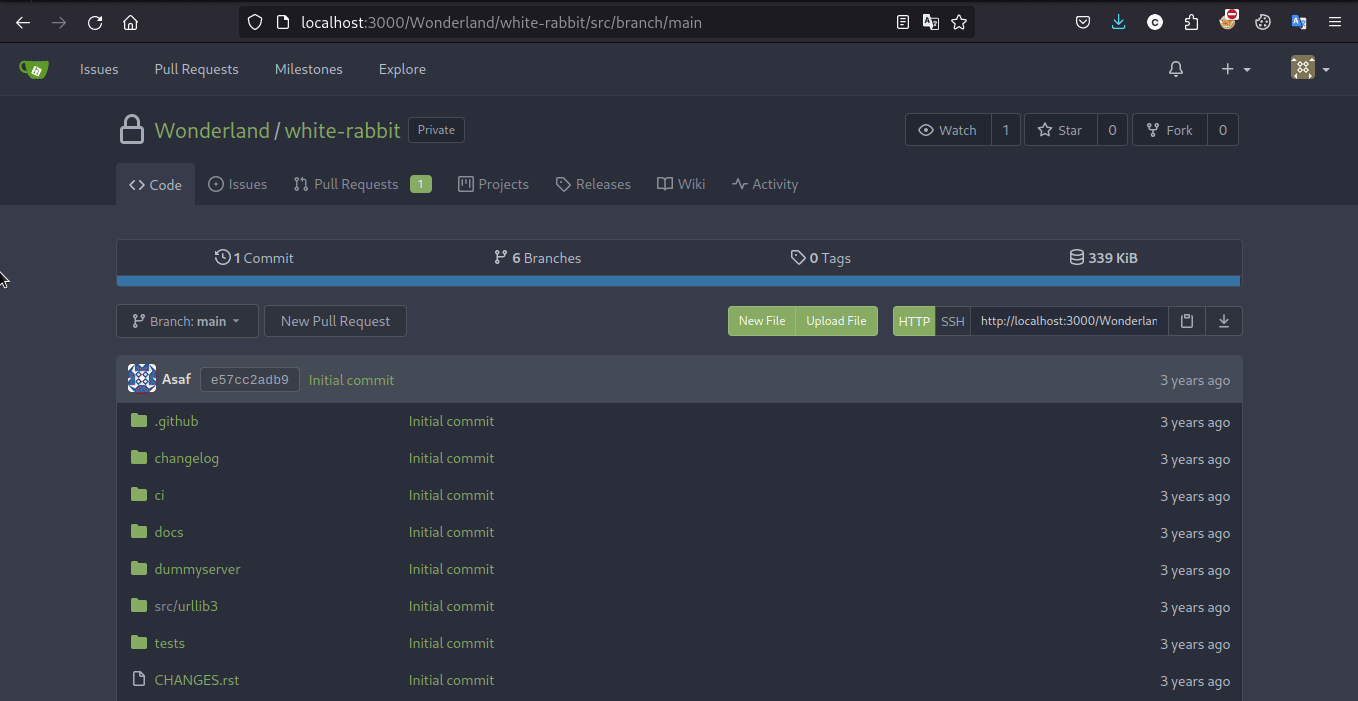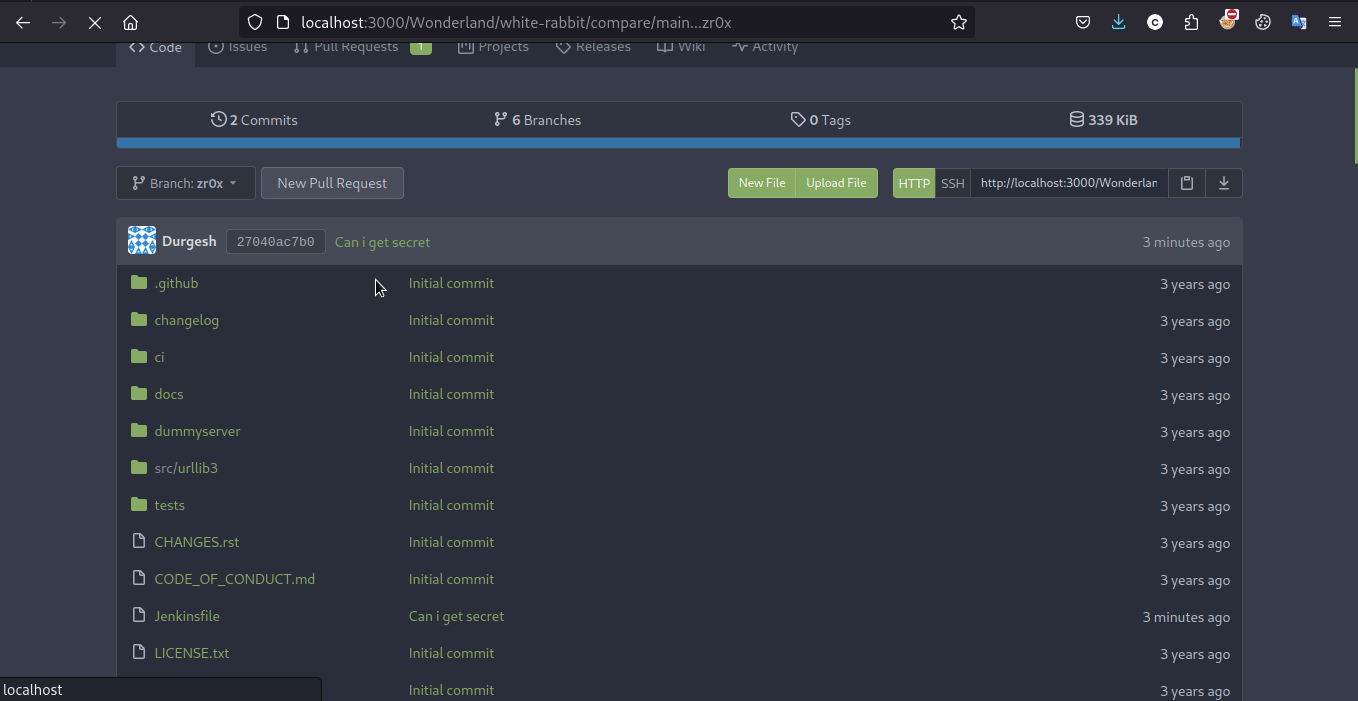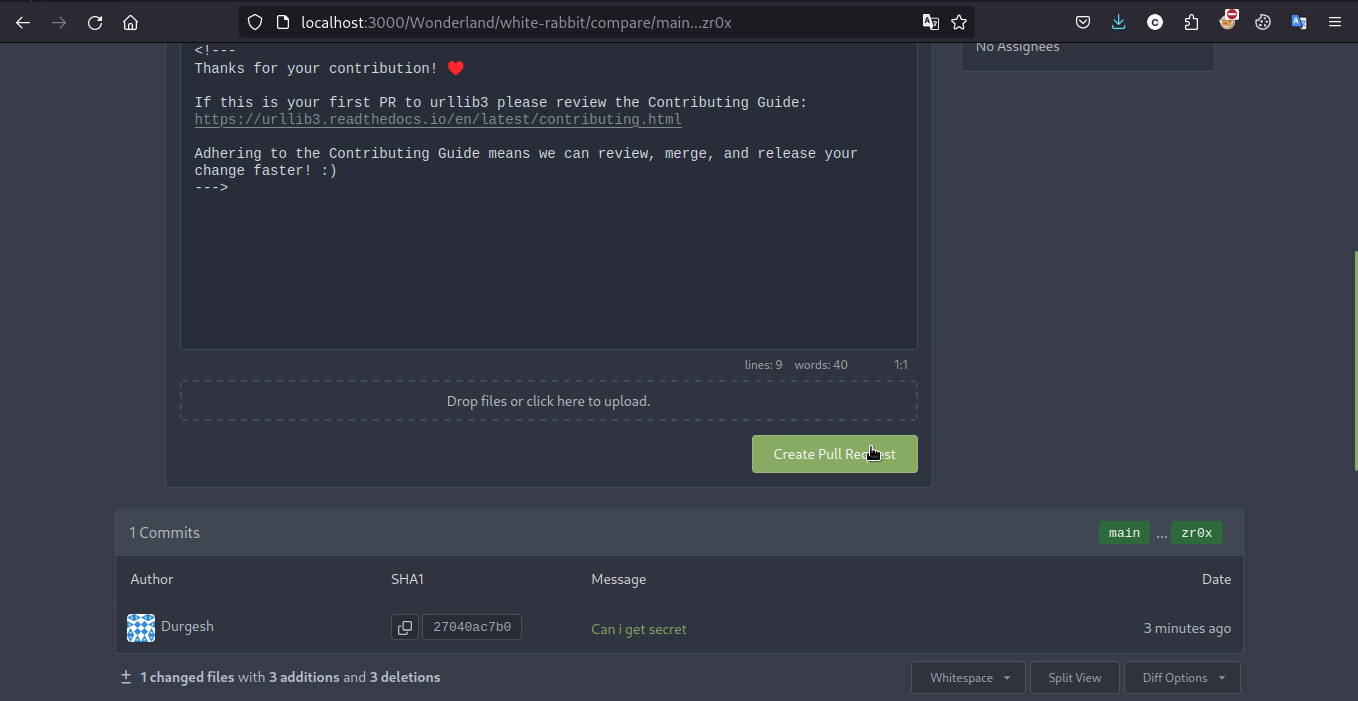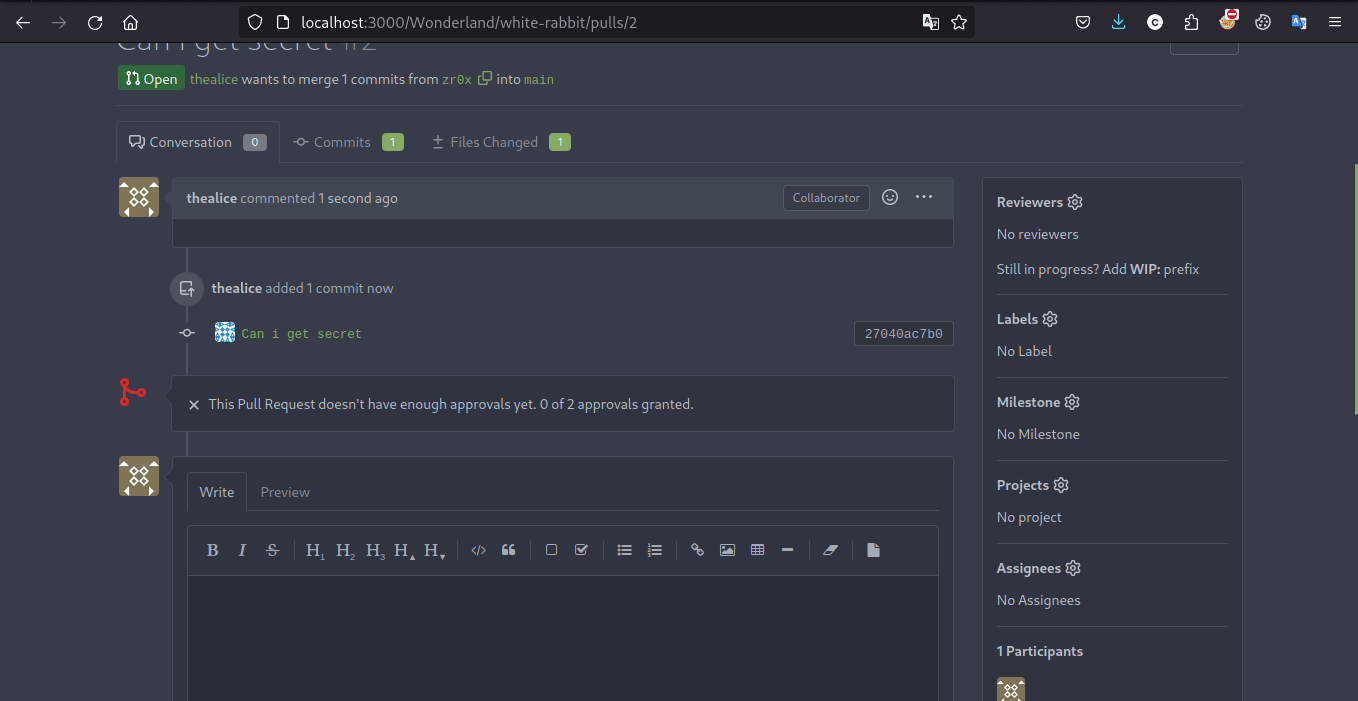
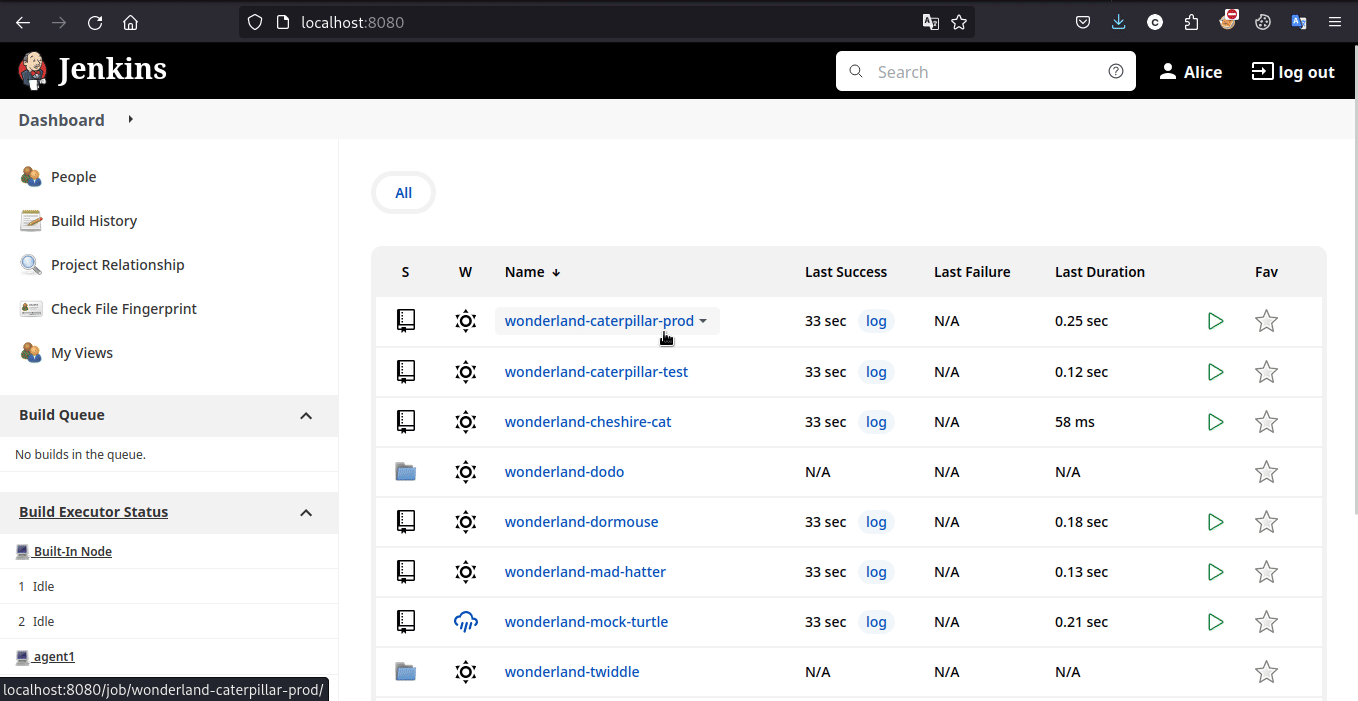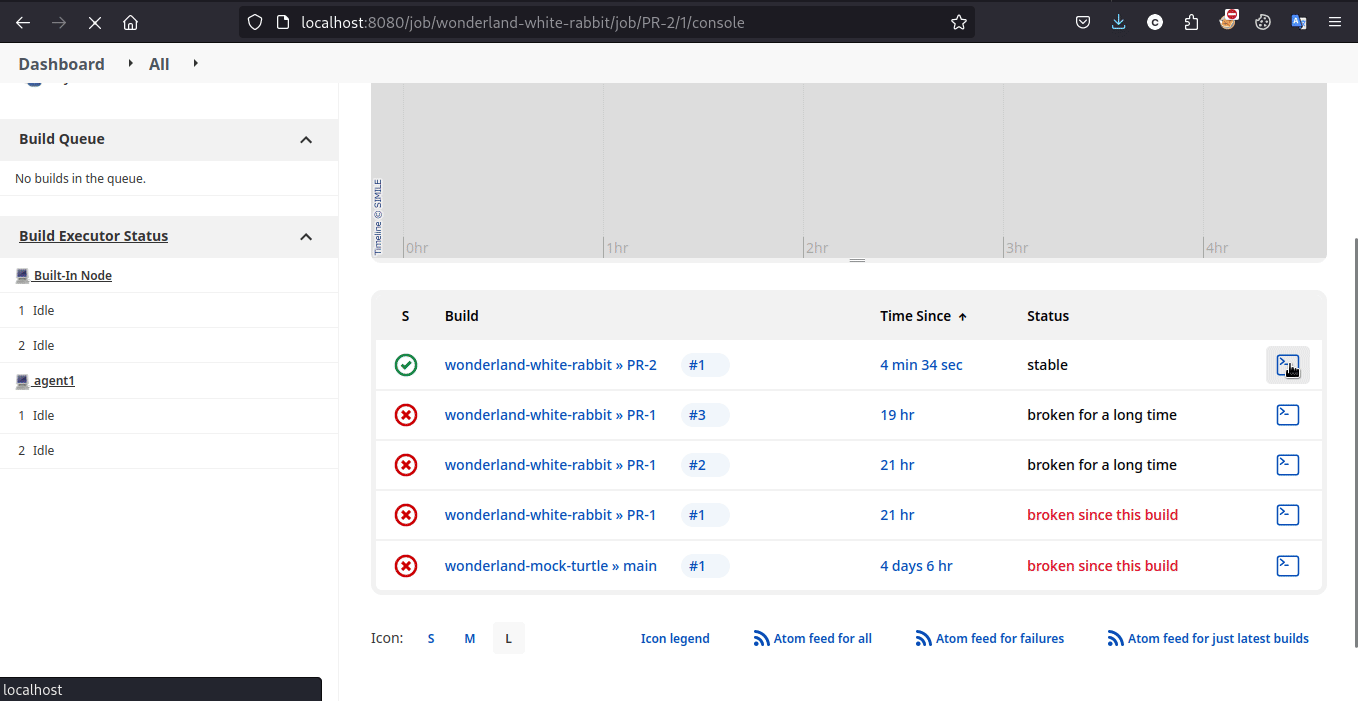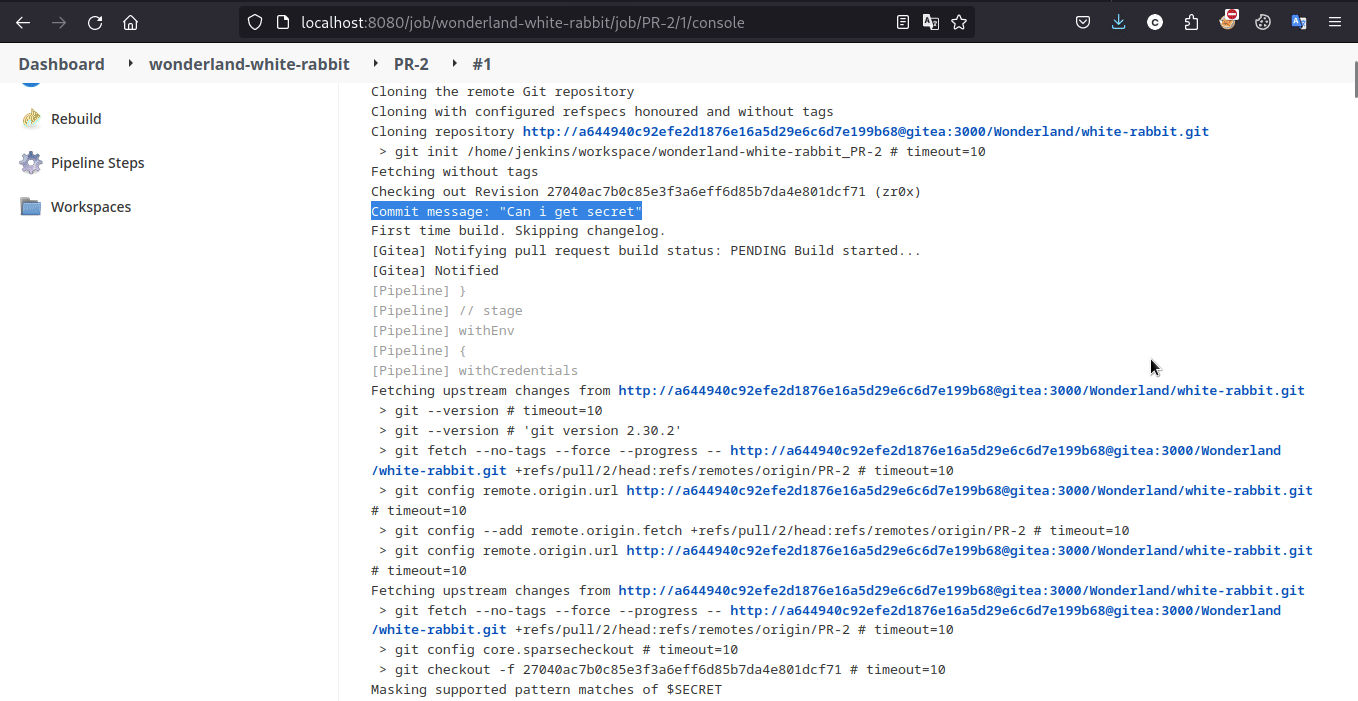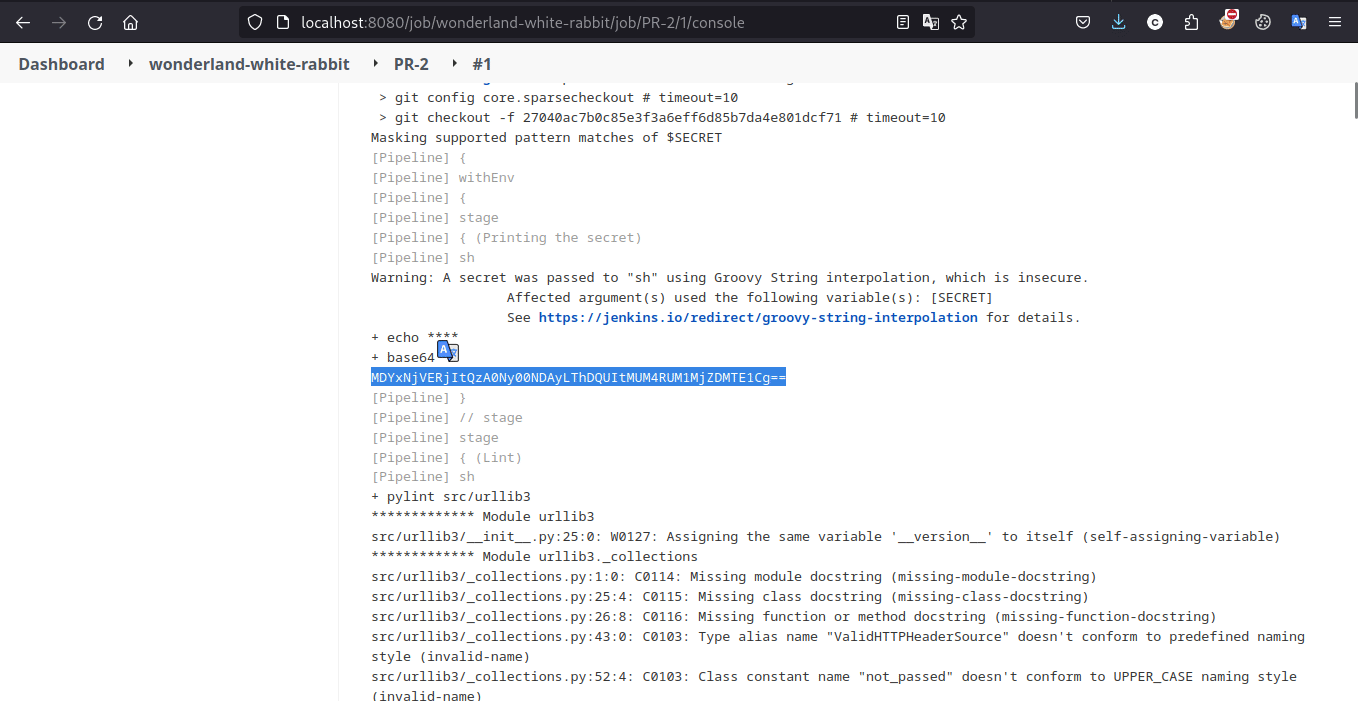
Exploit
1 | pipeline { |
Mad Hatter
Risks
- CICD-SEC-4: Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE)
- CICD-SEC-6: Insufficient Credential Hygiene
Analysis
本题与上一题的整体攻击思路类似,唯一的不同在于,本题的 Jenkins 文件被单独放在了其它仓库,并且我们不具备它的读写权限。因此,如果你直接重复上一题的步骤,将会在修改 Jenkinsfile 后进行 git push 时被拒绝。但是通过审计 Jenkinsfile 可以发现
1 | stage('make'){ |
此处 Jenkins 将执行 Makefile 中的命令,而 Makefile 的内容是我们可控的,因此可通过修改 Makefile 执行的命令间接控制 Jenkinsfile 中会执行的指令,实现间接 PPE (I-PPE)
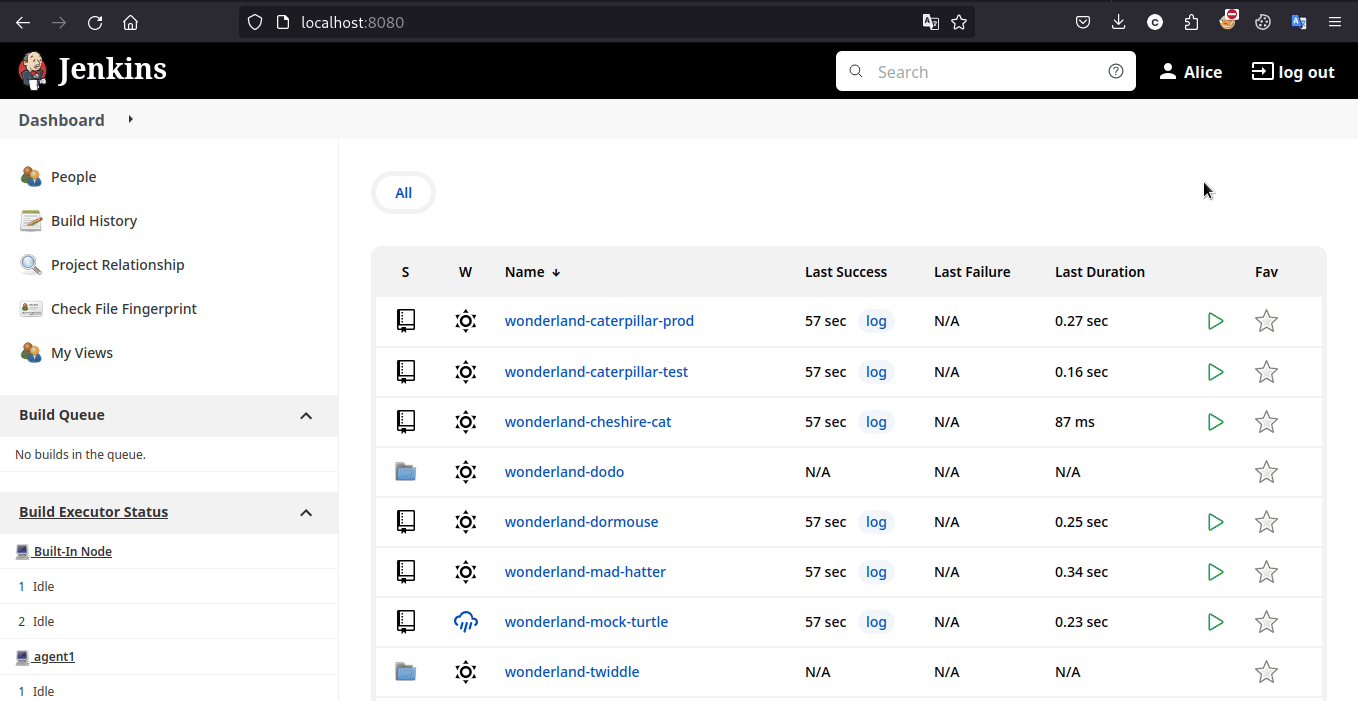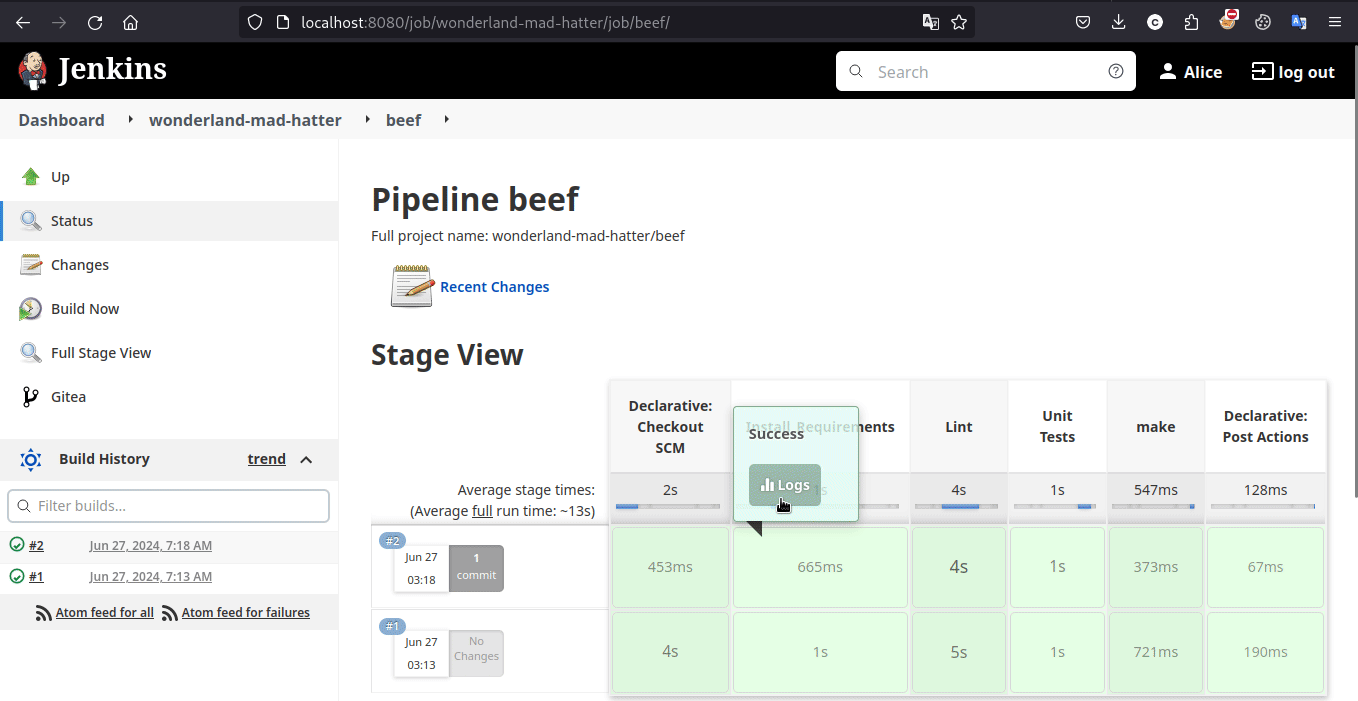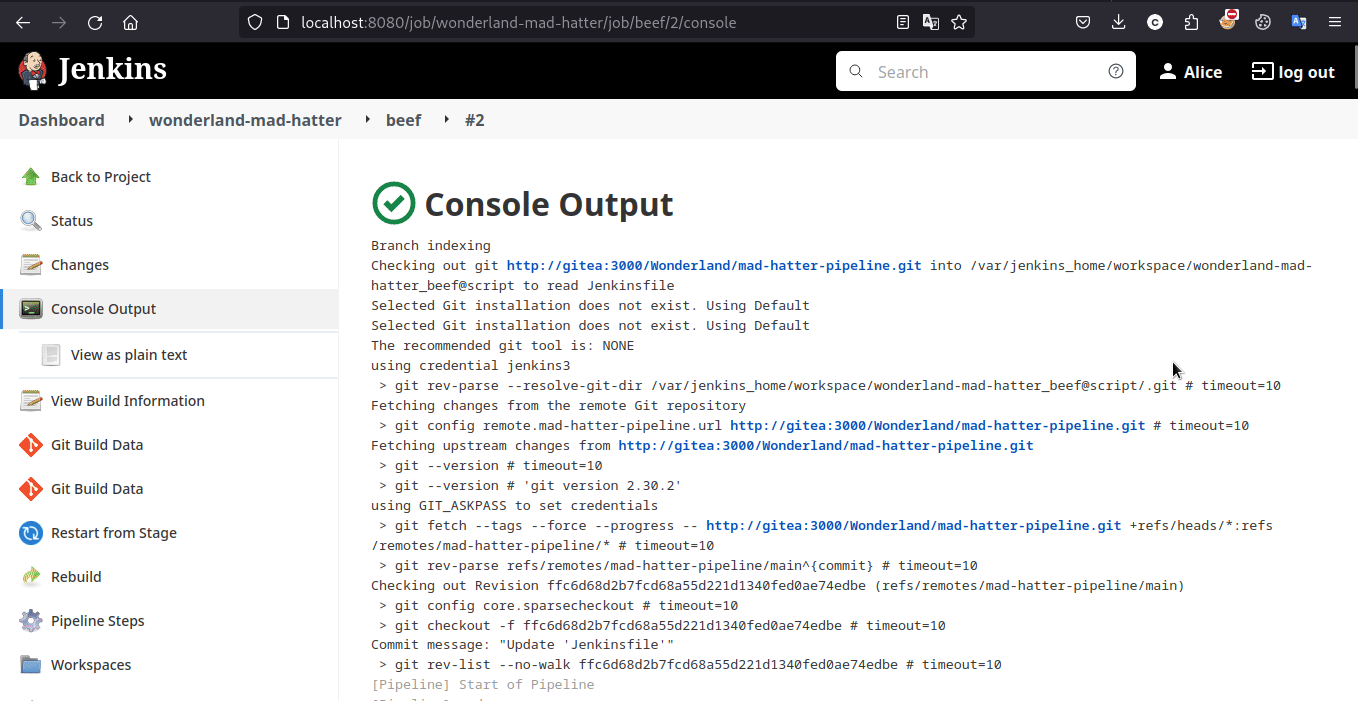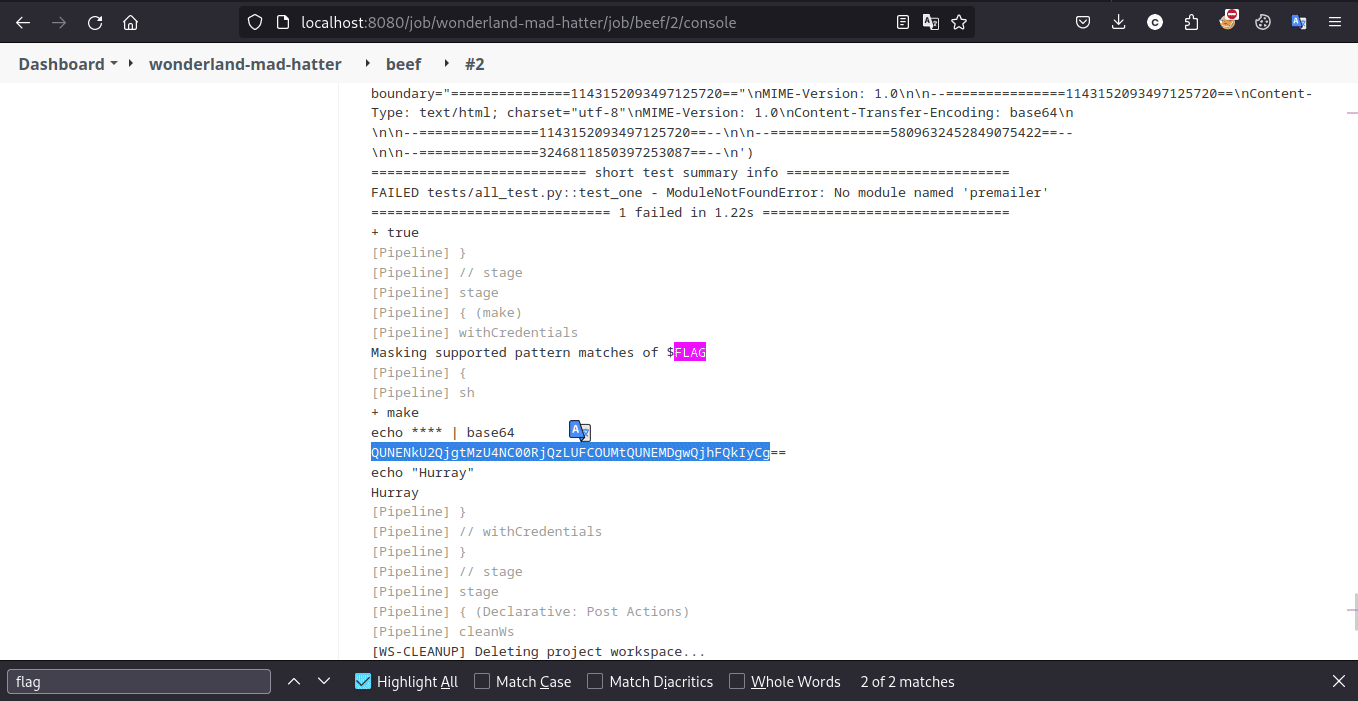
Exploit
1 | whoami: |
Duchess
Risks
- CICD-SEC-7: Insecure System Configuration
Analysis
这道题其实是 Web 安全的经典题,不过也确实和云安全相关。通过题目描述和 hint 能够意识到 git 仓库可能在某一次修改中存放了 PyPI 的 token,因此使用 Githack 和 Gitleak 或者干脆手动搜索的方式搜索题目给出的关键字即可拿到 Flag
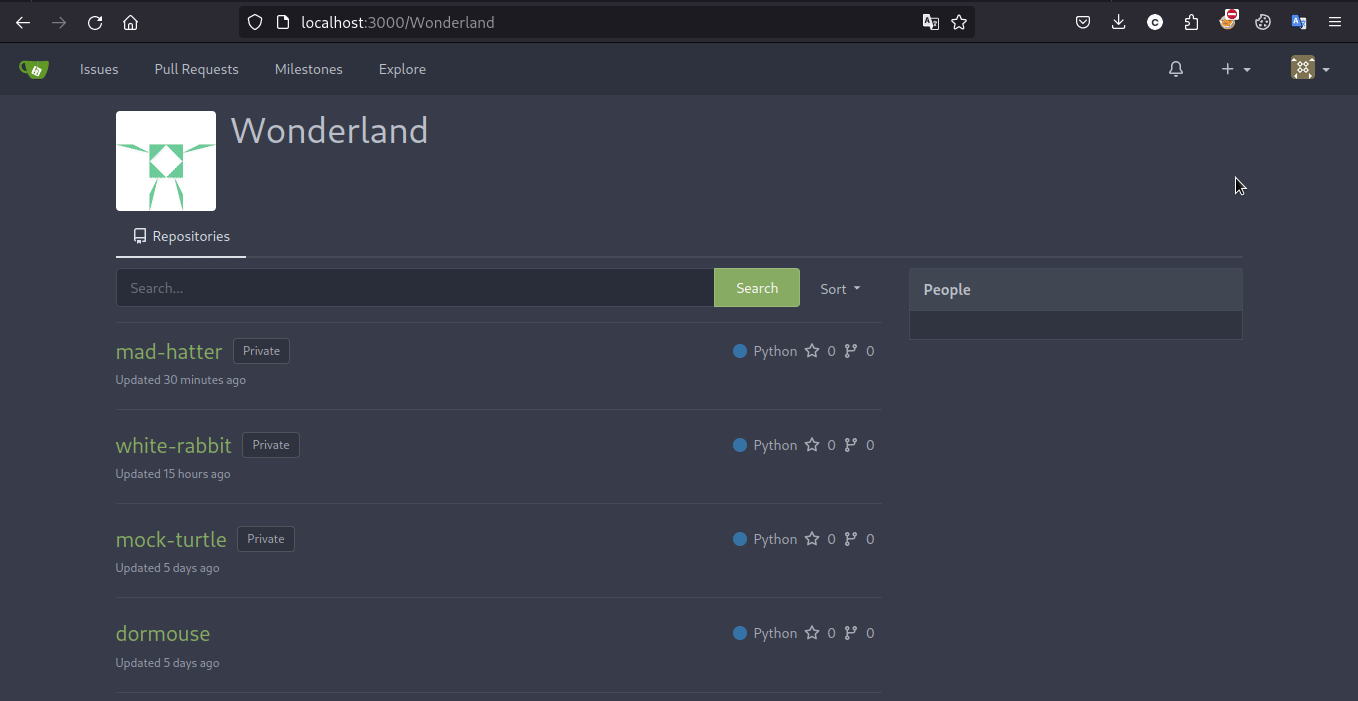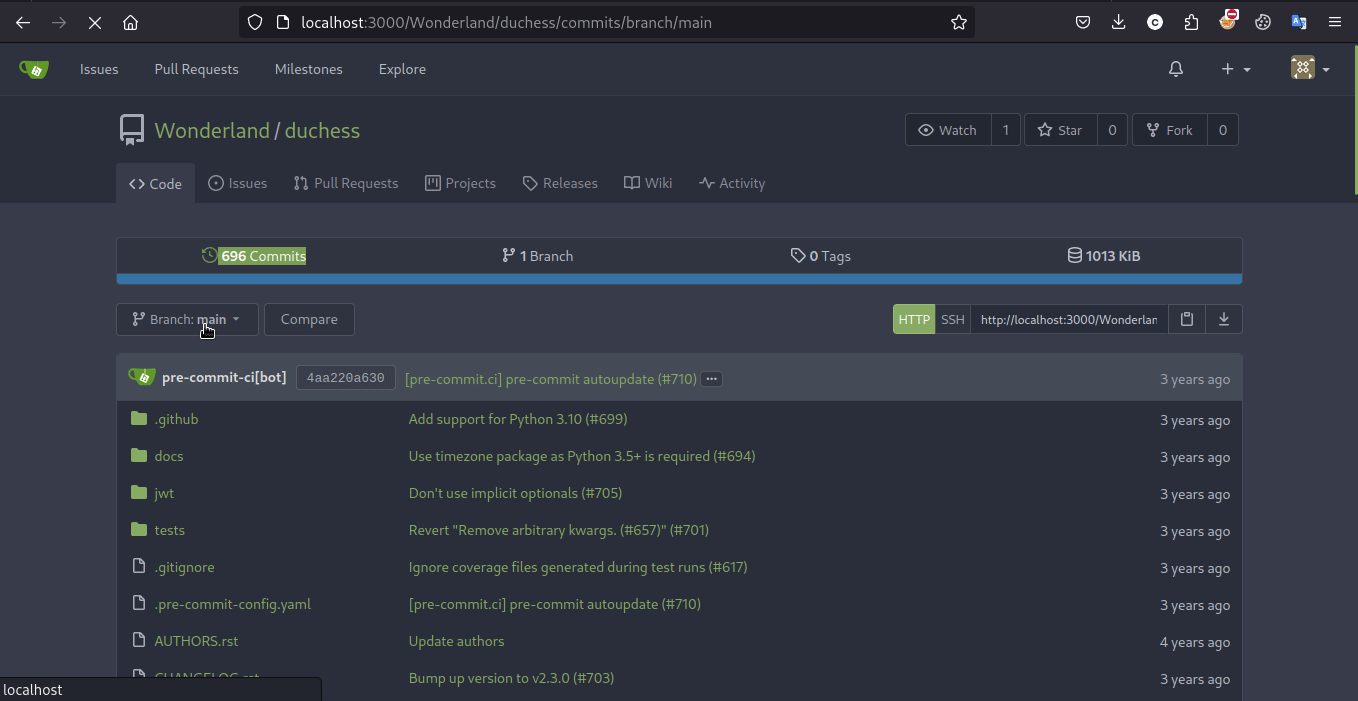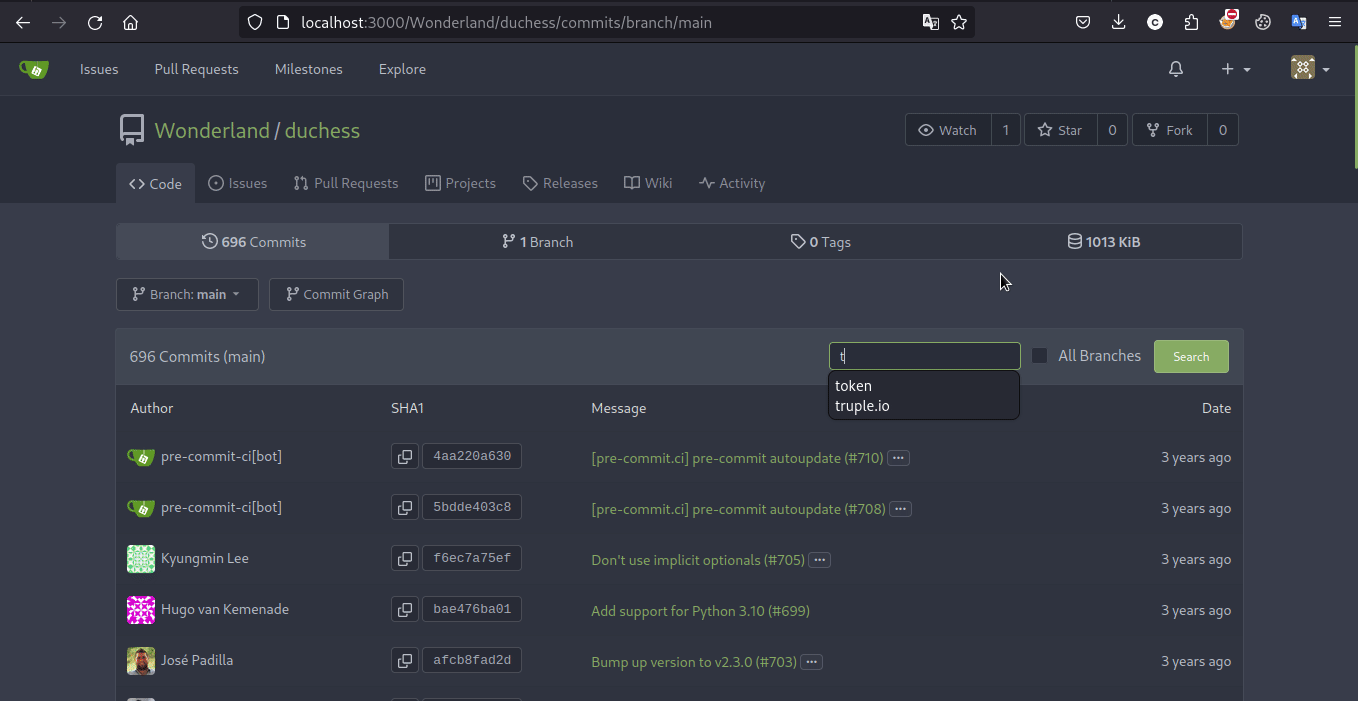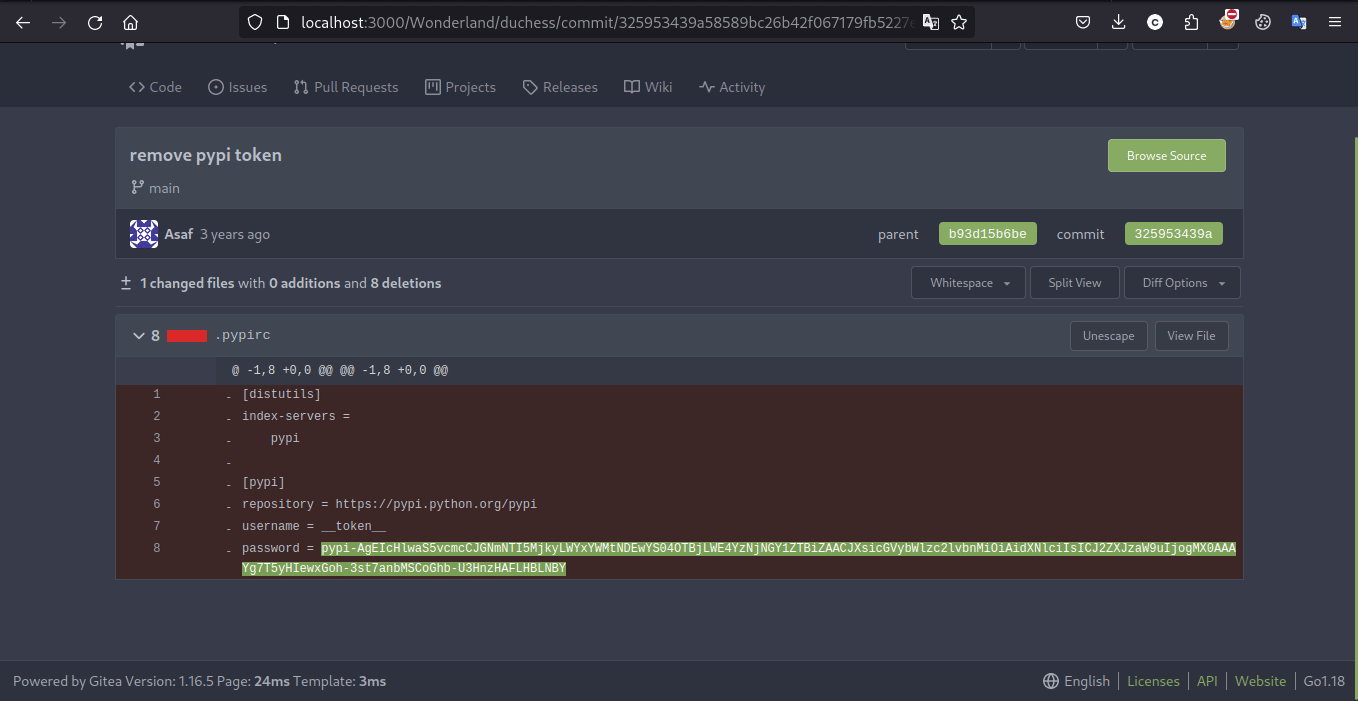
Exploit
1 | git show 43f216c2268a94ff03e5400cd4ca7a11243821b0 |
Caterpillar
Risks
- CICD-SEC-4: Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE)
- CICD-SEC-6: Insufficient Credential Hygiene
Analysis
审计 Jenkinsfile 时发现的
1 | stage('deploy') { |
这意味着想要读取 Flag 就必须要通过 main 分支触发的 CI/CD 流才能实现。不过这很好解决,直接把这个条件判断删除掉,但在 push 时又会发现攻击者不对该仓库具有读写权限。不过这依然不是难点,我们可以通过阅读 hint 解决,也就是不直接 clone 这个仓库,而是通过 fork 它到自己的仓库空间下使自己能够对自己 fork 来的仓库可读可写,再在修改 Jenkinsfile 后为原仓库提 Pr 触发 CI/CD 流。但是这样触发的 pipeline 输出 log 中不会有我们想要的 flag,阅读日志会发现
1 | ERROR: Could not find credential entry with ID 'flag2' |
事实上,在探索 Jenkins 控制台时,能够发现本题存在两条 pipeline 。而在 pr 时只会执行 wonderland-caterpillar-test 这一条 pipeline,而我们想要的 flag2 应该放在了 wonderland-caterpillar-prod 这一条 pipeline 的环境中
读名字能猜出来 test 是测试环境而 prod(product) 是生产环境,它们的生产管理实践可参阅 参考链接
参考提示 2,在测试 pipeline 中输出测试环境的所有环境变量,能够发现 GITEA_TOKEN,查阅一下它的作用,能够发现通过在 HTTP 标准认证使用它,攻击者就能够对上游源代码仓库进行读写,进而实现公共 PPE (Public-PPE / 3PE) 攻击
Exploit
在测试环境中
1 | pipeline { |
在生产环境中
1 | stage('deploy') { |
Cheshire Cat
Risks
- CICD-SEC-4: Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE)
- CICD-SEC-5: Insufficient PBAC (Pipeline-Based Access Controls)
- CICD-SEC-6: Insufficient Credential Hygiene
Analysis
这题照着 hint 做就行,直接 PPE 即可,与第一题的不同在于根据题目描述能够得知 flag 放在了用户根目录下,以及需要在 Jenkinsfile 的 agent 字段指定内置节点标签,搜索一下得知标签名为 built-in
Exploit
1 | pipeline { |
Twiddledum
Risks
- CICD-SEC-3: Dependency Chain Abuse
Analysis
ToDo (npm 没配镜像开摆了没做)
大体上通过攻击目标仓库的依赖仓库实现供应链投毒,进而对目标仓库进行 I-PPE
攻击原理参阅 参考链接
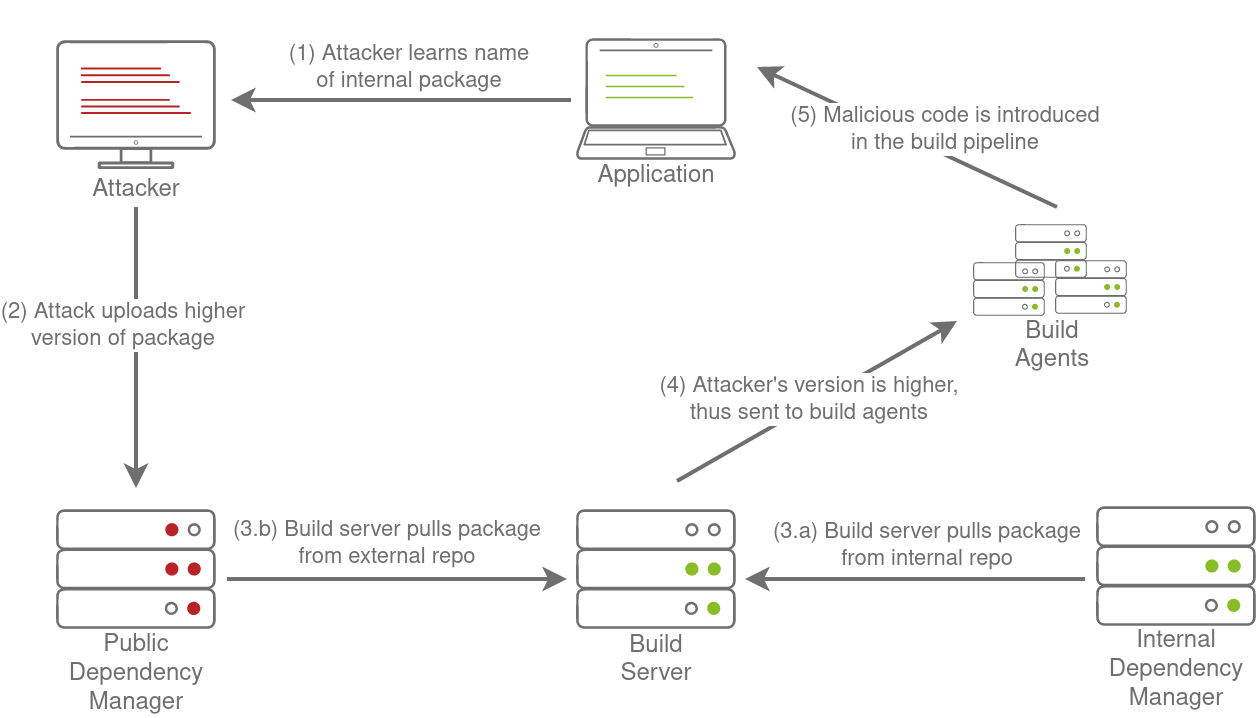
Exploit
Dodo
Risks
- CICD-SEC-1: Insufficient Flow Control Mechanisms
Analysis
Hint 给出了参考资料(Malicious Code Analysis 并建议了解 Checkov,后者是一个开源静态分析工具,旨在帮助开发人员和 DevOps 团队发现并修复基础设施即代码(IaC)中的安全和合规性问题。由 Bridgecrew 开发,支持各种 IaC 框架,包括 Terraform,CloudFormation,Kubernetes,ARM 模板等。它扫描 IaC 文件以识别错误配置、潜在漏洞以及对最佳实践的遵守情况。不出意外本题需要利用它的漏洞实现攻击或需要对它进行某种 Bypass。
在 Jenkins 控制台的输出中攻击者能够发现 Checkov 的扫描目标与扫描的配置
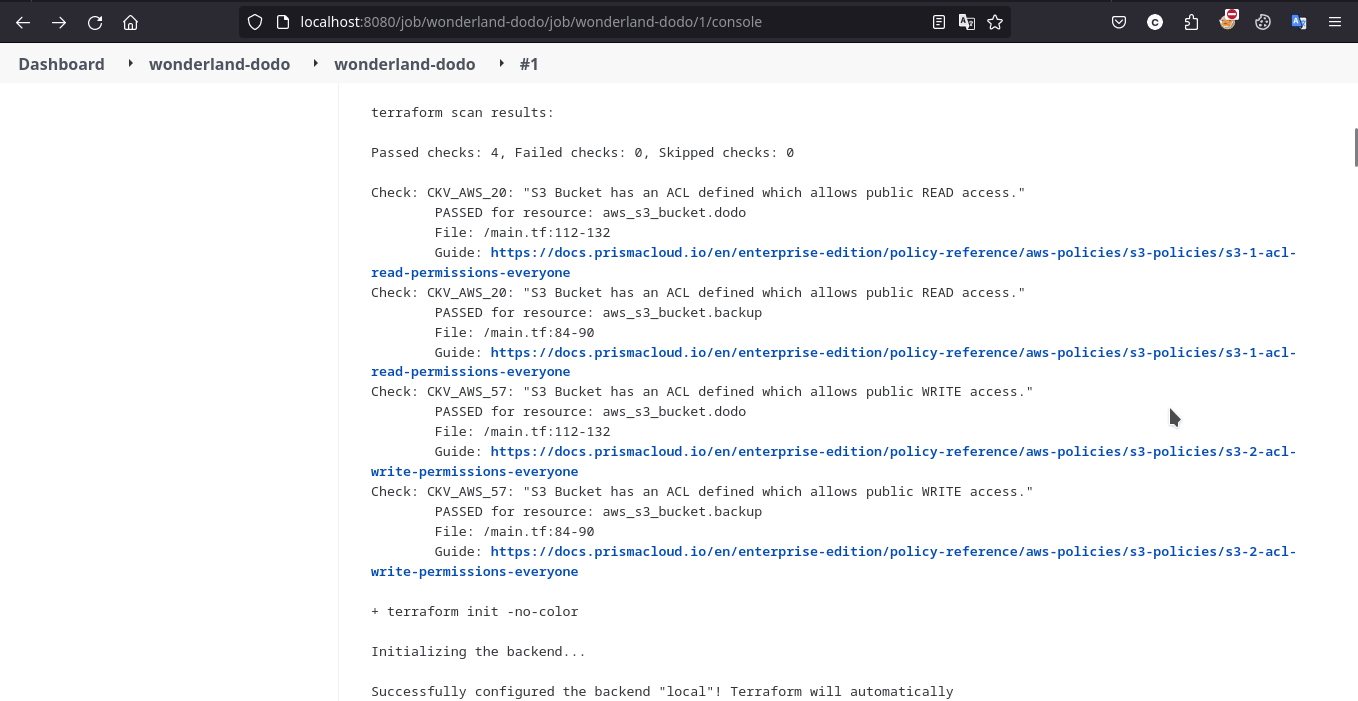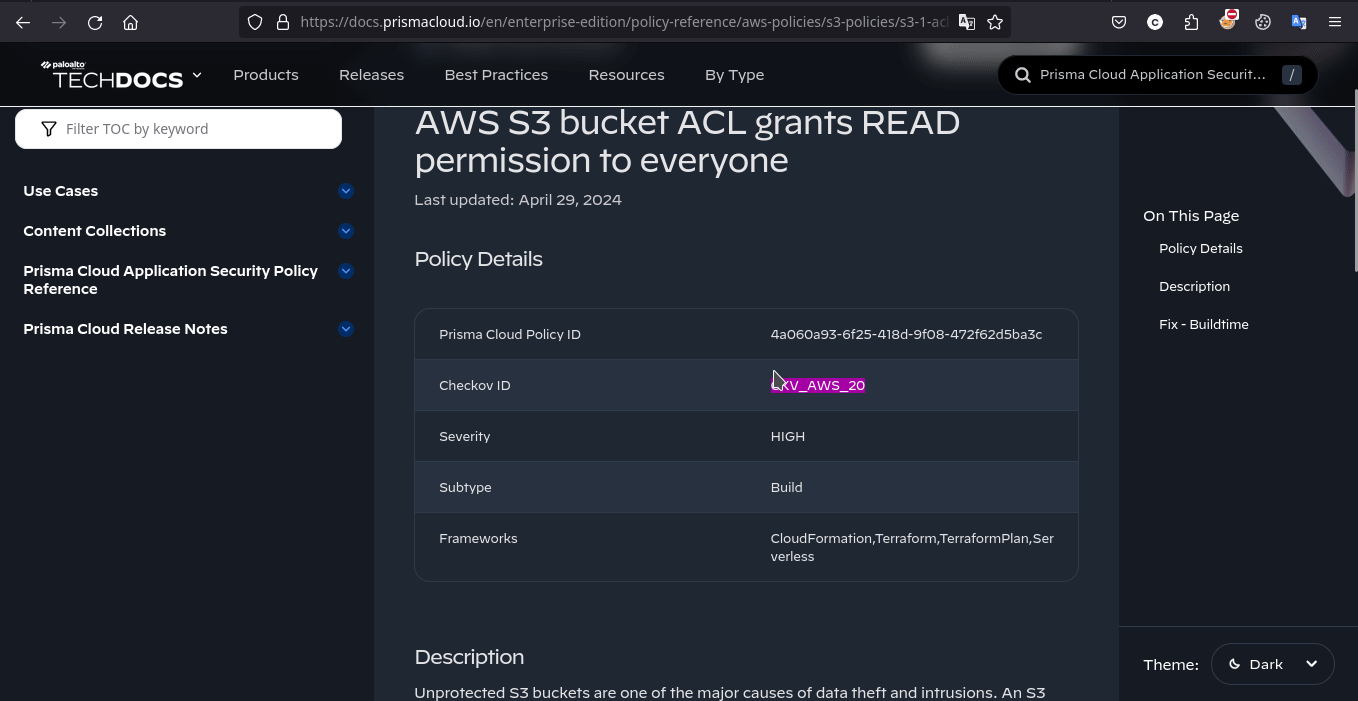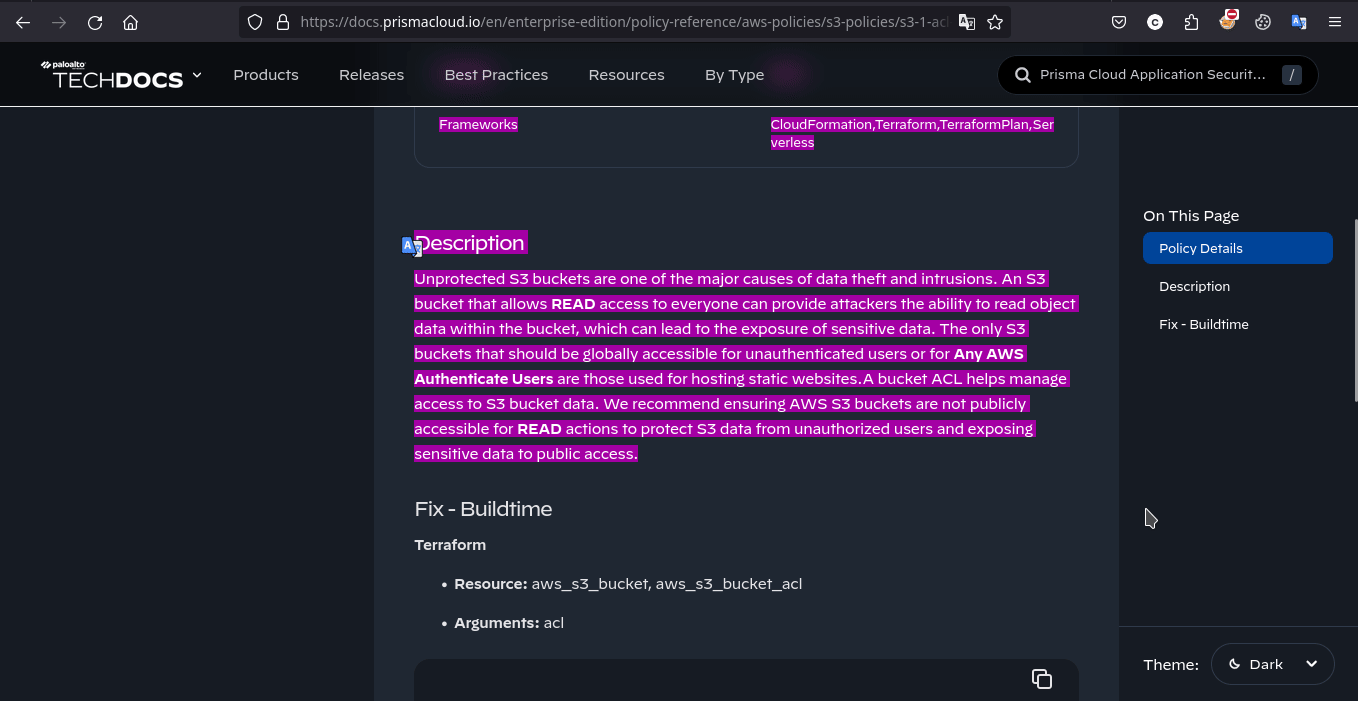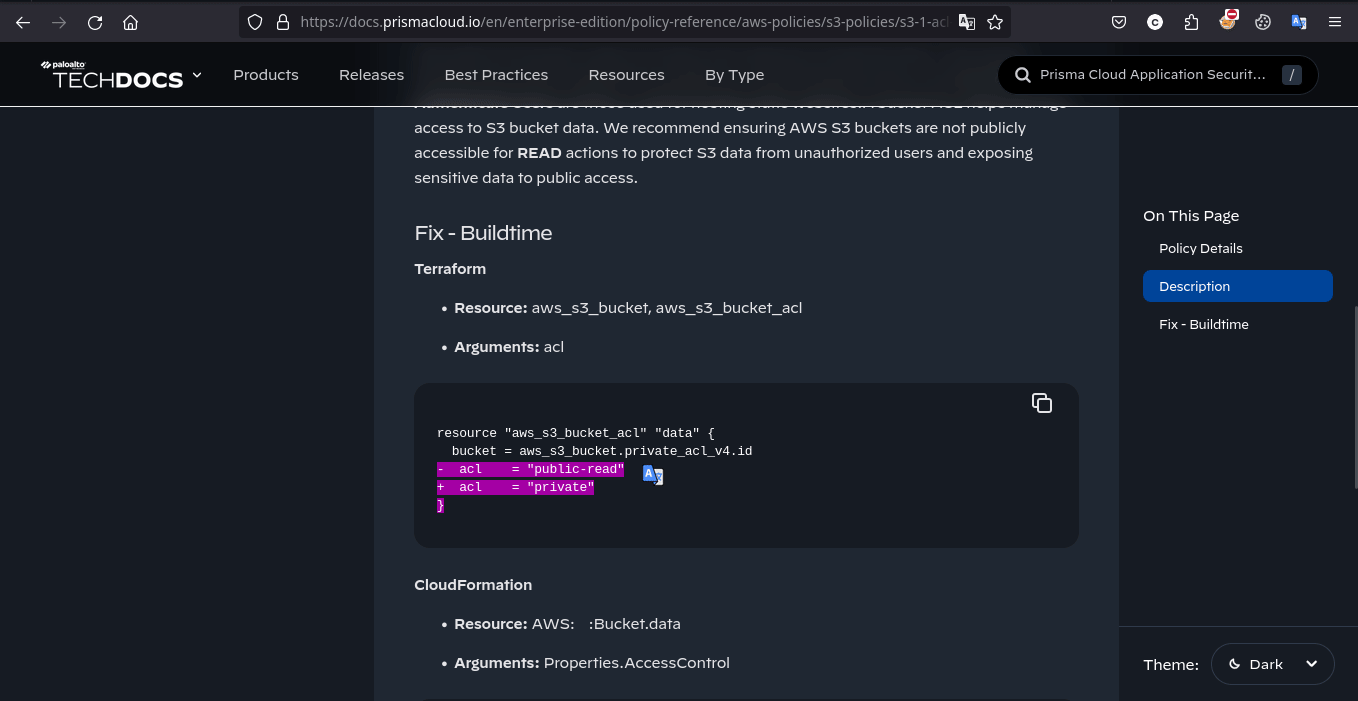
按照题目描述,本题需要创建 .checkov.yml 以自定义 Checkov 的行为,令其扫描本项目的配置文件时忽略 s3 bucket 公开可见这一配置不当实现 Bypass。具体步骤为修改 main.tf 令 S3 bucket 公开可见,并配置 .checkov.yml 忽略对其进行的扫描
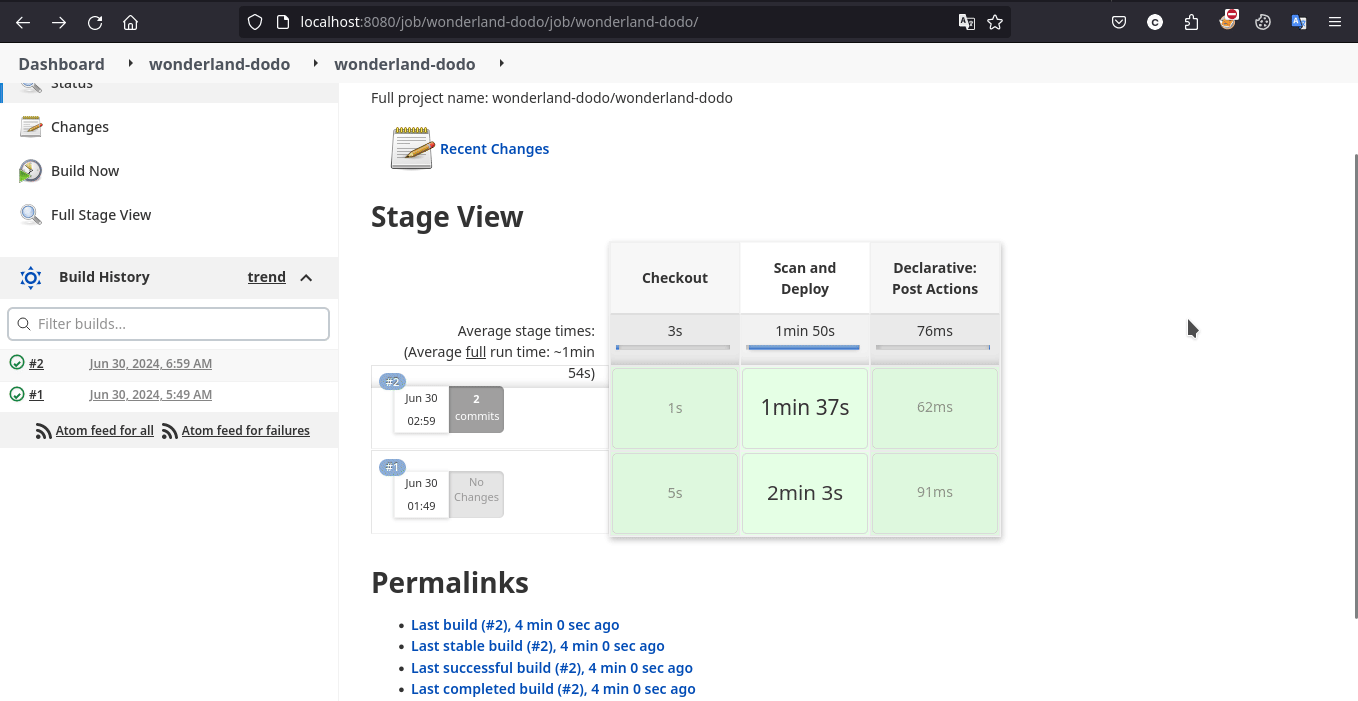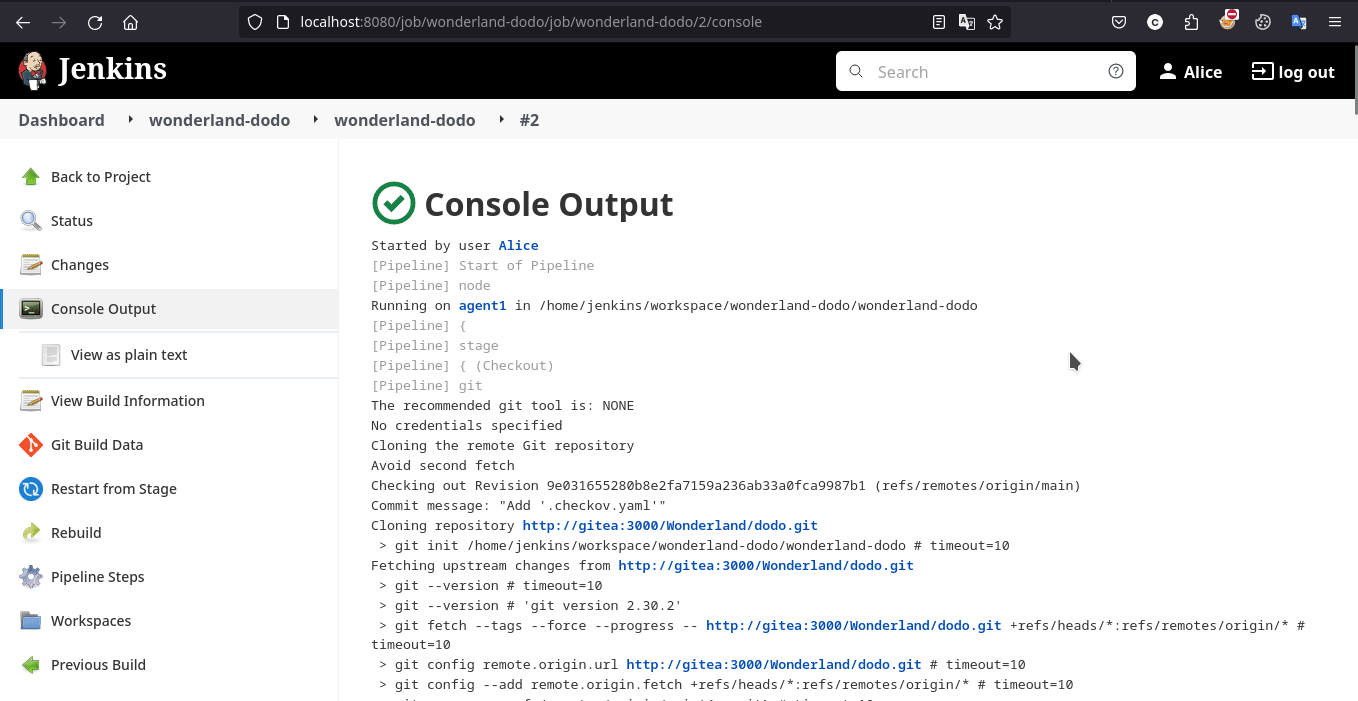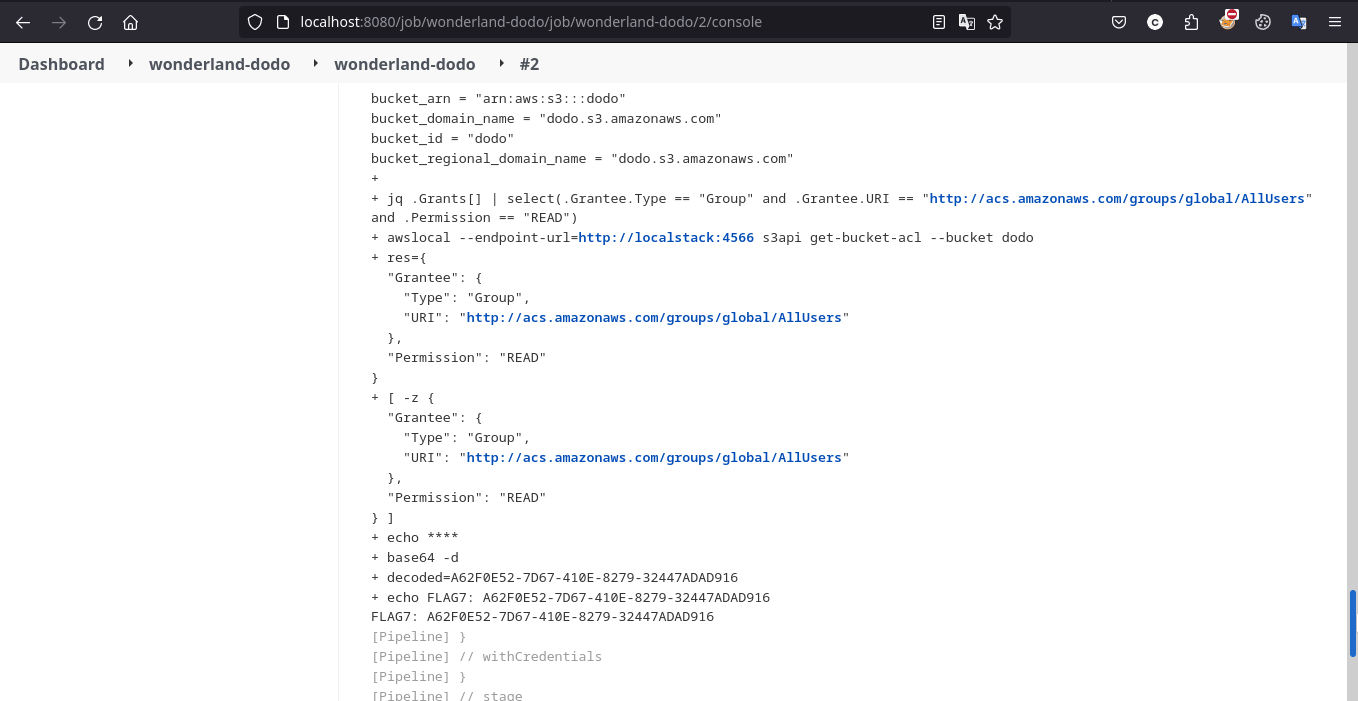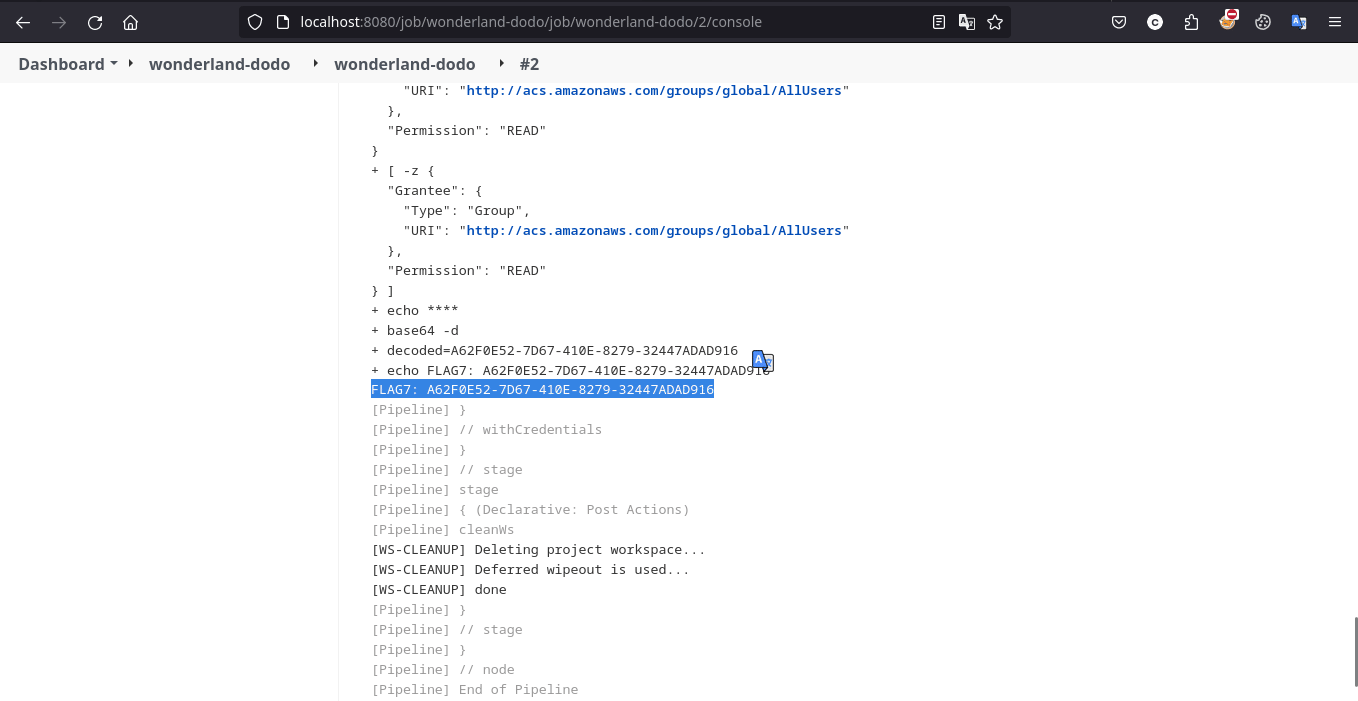
成功获得 flag
AWS S3 bucket 的配置文件的更多信息见 参考链接
Exploit
main.tf 中修改该行
1 | resource "aws_s3_bucket_acl" "data" { |
在 .checkov.yml 中写入
1 | soft-fail: true |
Hearts
Risks
- CICD-SEC-1: Insufficient Flow Control Mechanisms
Analysis
按照 hint 可爆破得到结点管理员的账号和密码。结点管理员可建立结点,而这些结点能够通过 SSH 服务互相连接,同时连接的目标可以由结点管理员指定。因此攻击者可以创建新的结点并指定结点去连接 SSH 蜜罐,进而获取结点使用的 SSH 用户名与密码,从而实现横向或纵向的进一步渗透
Exploit
1 | #使用任意 SSH 蜜罐皆可 |
Dormouse
Risks
Analysis
TODO 本题环境疑似有些残缺,没做
Exploit
Mock Turtle
Risks
- CICD-SEC-1: Insufficient Flow Control Mechanisms
- CICD-SEC-4: Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE)
- CICD-SEC-6: Insufficient Credential Hygiene
Analysis
挺传统 CTF 的一道题,先审计 Jenkinsfile
1 | pipeline { |
可以发现本题可以进行 D-PPE 攻击,不过通过 Pr 修改 Jenkinsfile 进行 D-PPE 攻击时需要先通过 pipeline 的 Pr check,具体上是 3 个检查
- 增加的单词数和减少的单词数必须相同
- version 文件只有一行,并且符合 x.y.z 的格式
- version 文件内容发生了更改
修改 Jenkinsfile 后去别的文件里增加 Jenkinsfile 里减少的字符数相等的字符数再让 version 文件的小版本号 +1 即可
Exploit
1 | pipeline { |
Grython
Risks
Analysis
ToDo 还没做
Exploit
Reference
CI/CD GOAT
OWASP Top 10 CI/CD Security Risks
What is CI/CD?
OWASP CI/CD Security Cheat Sheet
DevSecOps Outline
Jenkinsfile Syntax
PPE
sf4ult’s wp(gif 图来源)
Intro to pipeline automation
Dependency Management
S3 Bucket
Checkov
- Title: CI/CD GOAT Writeup
- Author: 7erry
- Created at : 2024-12-10 17:31:39
- Updated at : 2024-12-10 17:31:39
- Link: https://7erryx.github.io/2024/12/10/Tech Blog/CI-CD-GOAT-Writeup/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.